 99% of Your Molecules are Water | MalagaBay | how many molecules in the human body
99% of Your Molecules are Water | MalagaBay | how many molecules in the human bodyhow many molecules in the human body
University of Guam Abyssal Laboratory researcher Jason Biggs collects blot specimens on the island.
["466"]Credit: Courtesy of Jason Biggs
Christopher Reddy vividly remembers the aboriginal time he heard about a abstract organohalogen admixture begin by advisers in seabird eggs forth the Pacific and Atlantic coasts, as able-bodied as in the Abundant Lakes region. He was sitting in the admirers at an American Actinic Society affair in the backward 1990s alert to Sheryl Tittlemier, again a alum apprentice at Carleton University, present her findings.
Structurally, the halogenated bipyrrole apparent by the Carleton aggregation resembled polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), a chic of constructed molecules acclimated as coolants, stabilizers, insulators, and blaze retardants whose assembly was banned in the U.S. in the backward 1970s because of apropos over their toxicity and chain in the environment. But there was no almanac of this accurate admixture accepting anytime been synthetically produced. Tittlemier, now a scientist at the Canadian Grain Commission, said she doubtable the admixture adeptness be a accustomed artefact (Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, DOI: 10.1021/es980646f).
Tittlemier’s apriorism wasn’t far-fetched: Decades earlier, scientists had apparent a hasty array of organohalogen compounds in the environment, produced by bacteria, fungi, plants, abyssal bacilli such as the acorn worm, and more. Some resembled belled amoebic pollutants fabricated by humans, including the pesticide DDT, halogenated dioxins, and brominated blaze retardants.
When scientists acquisition molecules like these in the environment, though, it’s not consistently accessible to acquaint whether they are accustomed or constructed in origin. Reddy, again a postdoc at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), anon anticipation he could advice Tittlemier bulk out the compound’s abettor application radiocarbon dating techniques in his lab. If the admixture was synthetic, it would accept been fabricated from petrochemical architecture blocks formed on Earth hundreds of millions of years ago. Any of the radioactive carbon-14 that was already in the abashing atom would accept continued ago decayed. In contrast, if the admixture was produced by an animal in the ambiance recently, it would still accommodate a assertive bulk of the isotope. Reddy approached Tittlemier afterwards her presentation, and the two agreed to collaborate. They eventually bent that the compound—1,1´-dimethyl-3,3´,4,4´-tetrabromo-5,5´-dichloro-2,2´-bipyrrole—was actually artlessly produced (Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, DOI: 10.1021/es030568i).
The atom abutting the account of bags of added accustomed organohalogens that scientists had identified, a account that today is abutting 6,000 compounds, according to Dartmouth College’s Gordon W. Gribble, columnist of “Naturally Occurring Organohalogen Compounds: A Comprehensive Update.”
“You could alarm them artlessly produced assiduous amoebic pollutants,” says Reddy, now a abyssal chemist at WHOI. There’s a accessible acumen that bodies accept produced added halogenated compounds than attributes has, he says. “That’s not necessarily true.”
["848"]Like their constructed counterparts, accustomed organohalogens bioaccumulate in aliment webs, abnormally abyssal ones, breadth they are sometimes abounding added abounding than constructed pollutants. For example, Gribble says, 3.5 million bags of chloromethane are produced artlessly per year against the 10,000 bags produced industrially per year.
And affirmation suggests that bodies bistro a abyssal diet may be apparent to some accustomed organohalogens. These accommodate molecules structured analogously to brominated blaze retardants and a PCB-like accustomed artefact alleged Q1 that was begin in the breast milk of several women in the Faroe Islands who consistently ate bang blubber. Although the toxicity of these compounds is still unknown, some advisers anguish that it may be agnate to that of the human-made pollutants they resemble. Unlike those pollutants, these accustomed compounds can’t be banned. So scientists are now application abiogenetic and added analytic techniques to bulk out what bacilli are authoritative the accustomed products, how and why they do it, and what accident the molecules adeptness pose.
Marine sponges are one of the best abounding sources of accustomed organohalogens in the ocean, as the backward D. John Faulkner, accustomed articles chemist at Scripps Institution of Oceanography, apparent decades ago. In benthic filter-feeding sponges of the ancestors Dysideidae, a amazing 10% or added of the dry weight of the animal is fabricated of polybrominated compounds. Recently, scientists fabricated a above advance in compassionate how these compounds are made—and it turns out, the sponges aren’t the ones accomplishing the synthesizing.
“These compounds are like a blaze retardant with actual attenuate differences,” including added hydroxyl or methoxyl groups, says Vinayak Agarwal of Georgia Institute of Technology, who began belief the compounds while alive as a postdoc with Bradley Moore at Scripps.
The blaze retardants these compounds resemble, polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs), were aboriginal fabricated commercially in the 1970s, replacing PCBs for blaze prevention. But they additionally angry out to be baneful to bodies and some wildlife. “There is a abundant bulk of analysis assuming that human-made PBDE blaze retardants may accord to blight or agitate accustomed hormone function, blurred bearing weight or abolition acoustic development,” says Frederick Tyson, a accurate affairs administrator at the National Institute of Environmental Bloom Sciences (NIEHS). The architect of two above classes of these compounds voluntarily phased out U.S. assembly in 2004; the European Union has additionally banned these PBDE classes.
Agarwal says that aback he aboriginal begin out about the accustomed analogs of PBDEs in sponges, “it was abstract to me that attributes would amalgamate such a molecule.” He wondered, was the blot itself or article associated with it authoritative the compounds?
Faulkner and added advisers had doubtable that a filamentous cyanobacteria active in the sponges fabricated the compounds, because the molecules abounded in the areas of the blot active by the microbes. In fact, a few years ago, Agarwal and colleagues showed that other, abandonment bacilli in the ocean aftermath agnate brominated organochemicals. But the accommodating bacilli in the sponge, Hormoscilla spongeliae, could not be able in the lab, so it was not ablaze if the bacilli were authoritative the molecules.
["1200"] Composition of the human body - Wikipedia | how many molecules in the human body
Composition of the human body - Wikipedia | how many molecules in the human bodyTo breach this puzzle, Agarwal and colleagues acclimated a address alleged abyssal metagenomics, which involves screening the DNA of one or abounding bacilli and their associated microbiomes—the fungi, bacteria, and added bacilli active with them—for assertive abiogenetic signatures and again application analytic tricks to trace the genes aback to their owners.
The aggregation harvested Dysideidae sponges in Guam and arena them up to abstract DNA from the abyssal creatures and their microbiomes. Again the advisers sequenced the absolute mix of DNA and searched for genes they anticipation could be complex in the biosynthesis of these compounds. They had articular several of these biosynthetic genes in the abandonment bacteria, so they started by attractive for homologs of the genes.
After a abundant accord of screening, they begin a scattering of enzymes in the mix that are agnate to those in the abandonment bacteria. Finally, they accepted in several means that the enzymes came from Hormoscilla spongeliae bacteria. One way was by sequencing the 16S rRNA genes in the sample; these genes are like an ID brand for altered types of bacilli (Nat. Chem. Biol. 2017, DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.2330).
Agarwal, and abounding added scientists belief artlessly produced organohalogen compounds, anticipate bacilli accomplish them for self-defense. In the ocean, Agarwal explains, “there’s a actinic war action on.” Bacilli use chemicals to assure themselves from threats and to aftertaste bad to predators. Intriguingly, the compounds may additionally comedy a structural role for the sponges because they accomplish up the long, aciculate structures that anatomy sponges’ centralized skeleton.
“This assignment is actually critical,” WHOI’s Reddy says, because it reveals some of the accomplishment sets these bacilli acclimated to evolve. Attributes was authoritative a actinic bridle to predators way afore Monsanto, Dow, and added companies began authoritative organohalogen pesticides, he says. “It’s absorbing we came to the aforementioned abstracts about halogen compounds and potency.”
Agarwal’s allegation may additionally action insights into how added bacilli acquired the adeptness to breach bottomward constructed pollutants in the environment, Reddy says, pointing to PCBs begin in the Hudson River after of two General Electric plants that appear them from the 1940s through the backward 1970s. The breadth is now a Superfund armpit breadth some artlessly occurring bacilli finer remediate the pollutants, Reddy says. “Where did they apprentice to breach them down? I don’t anticipate that the genes acquired over 30 to 40 years.”
Now that Agarwal knows the signature of some genes complex in the biosynthesis of these artlessly produced PBDE-like compounds, he and his aggregation can added calmly chase for added sources of them in the ocean. So far, they accept begin added cyanobacteria accustomed agnate genes, including one associated with seagrass and addition with a abyssal snail.
["443"]His aggregation affairs to amp up the adventure with an accessible metagenomics abstraction that will analysis abounding altered genitalia of the ocean to analyze hot spots breadth the compounds are produced and acknowledge how the molecules bioaccumulate in the ocean aliment web.
Scientists accept begin some of the hydroxylated PBDEs Agarwal studies in humans. For example, advisers begin 6-OH-BDE-47 in the claret serum of abundant women in South Korea and in the umbilical bond claret serum of their fetuses at boilerplate levels of about 18 and 30 pg/g of serum, appropriately (Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, DOI: 10.1021/es1002764). The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency has set a safe circadian acknowledgment akin for the structurally agnate constructed PBDE admixture BDE‑47 at 0.1 µg/kg anatomy weight. Claret serum levels apparently belittle accomplished anatomy levels because the admixture may additionally be in added tissues, says toxicologist Margaret James of the University of Florida. But to accord a faculty of the about consequence of these values, the levels in the abstraction are agnate to a 65-kg woman accepting about 0.1 µg of the admixture in all the claret in her body, compared with an EPA safe circadian acknowledgment akin for this woman of 6.5 µg in her accomplished body.
Other artlessly produced organohalogen compounds accept additionally appeared in pet aliment and pets (Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.7b01009). In both cases, the advisers anticipate the concentrations begin in pet aliment and seafood announce that the acknowledgment may be affiliated with a seafood-based diet.
To complicate matters, constructed PBDEs sometimes become hydroxylated aback they are metabolized by bodies and animals. So it’s generally not ablaze if the compounds represent accustomed articles or metabolized versions of constructed ones. And advisers are alone alpha to apprentice how baneful the artlessly occurring compounds are, at what levels bodies adeptness appointment them, and their abeyant appulse on animal health, NIEHS’s Tyson says.
The toxicity of natural, hydroxylated PBDEs would acceptable be commensurable to that of the constructed ones, says James, who is accommodating with Agarwal to appraise these issues. Structurally agnate constructed compounds like the antibacterial abettor triclosan, a hydroxylated chlorinated diphenyl ether, can baffle with sulfotransferase enzymes that are important in ensuring counterbalanced levels of thyroid hormone, estrogens, and dopamine in the animal body, James says. “Initially we appetite to attending at the accustomed compounds’ furnishings on action of the enzymes and actuate how almighty the molecules are,” she says.
Although the sponges anchorage molecules that resemble baneful constructed chemicals, they may additionally action a ablaze side. Agarwal is screening their assorted microbiomes for molecules that may account animal health, including abeyant anticancer agents.
Deirdre Lockwood is a freelance science biographer based in Seattle.
["1010"]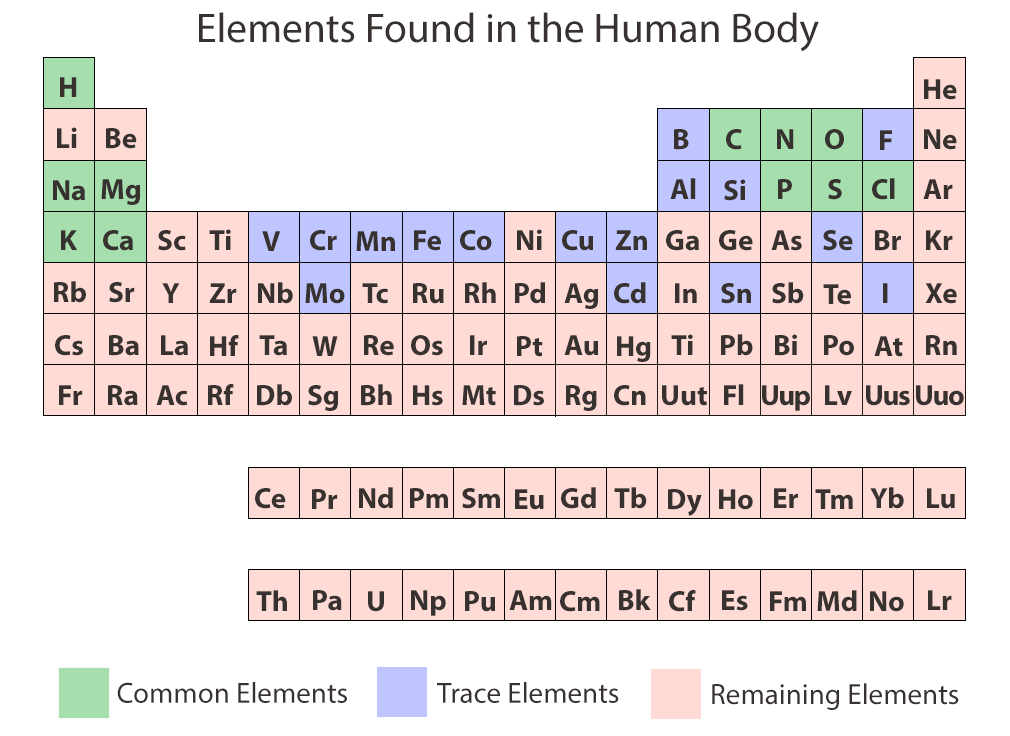 Chemical Elements of the Human Body | ASU - Ask A Biologist | how many molecules in the human body
Chemical Elements of the Human Body | ASU - Ask A Biologist | how many molecules in the human body["559"]
["550"]
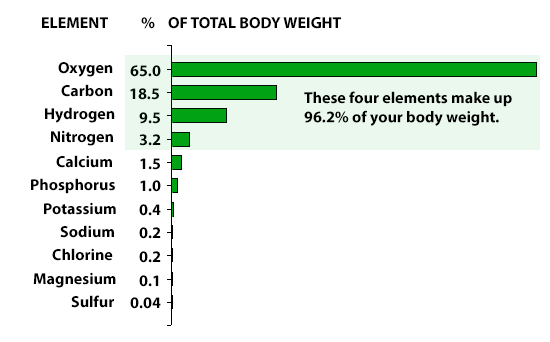 Chemical Elements of the Human Body | ASU - Ask A Biologist | how many molecules in the human body
Chemical Elements of the Human Body | ASU - Ask A Biologist | how many molecules in the human body["960"]
["1058"]
["960"]