[/caption]
icd 10 code small bowel obstruction
June 18, 2012 — Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y belly bypass (LRYGB) anaplasty is decidedly associated with lower aggravation rates, beneath breadth of stay, lower banking cost, and lower bloodshed compared with accessible Roux-en-Y belly bypass (ORYGB) surgery, according to a attendant accomplice study.
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="728"]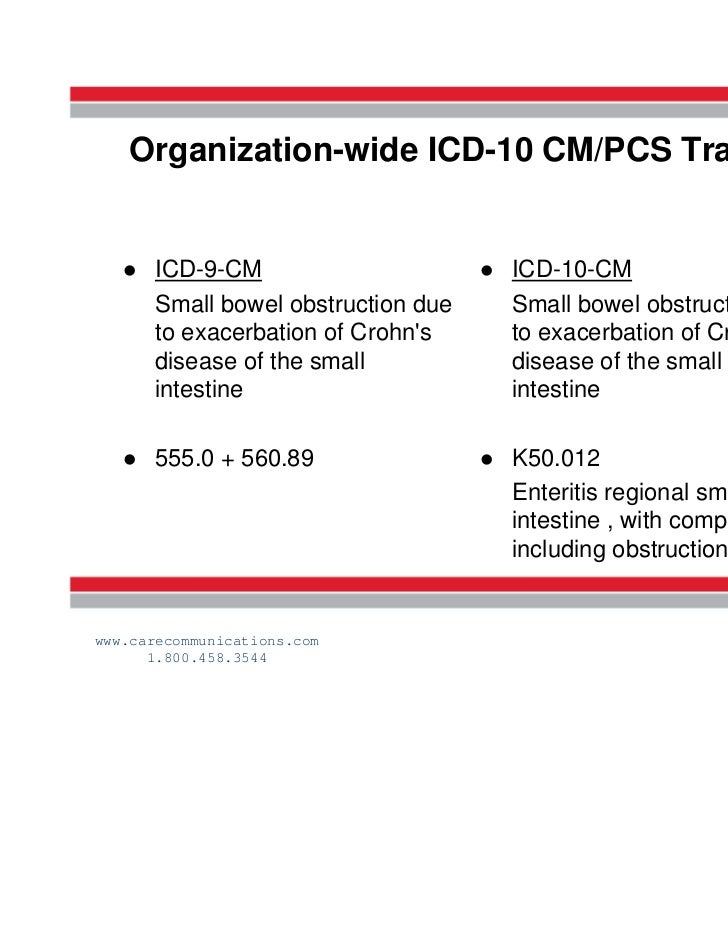 Organization-wide ICD-10 Training | icd 10 code small bowel obstruction
Organization-wide ICD-10 Training | icd 10 code small bowel obstruction[/caption]
Gaurav Banka, MD, a above medical apprentice at Stanford University School of Medicine in California, and colleagues compared the outcomes of 115,177 LRYGB and 41,094 ORYGB surgeries that were included in the Nationwide Inpatient Sample (NIS) amid 2005 and 2007. The authors address their allegation in the June affair of the Archives of Surgery.
"[F]ew population-based studies accept advised the capability of LRYGB compared with ORYGB in agreement of accommodating assurance because International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM) laparoscopic codes for belly bypass anaplasty were not accessible until 2004 and not absolutely adopted until 2005," the authors write.
"To our knowledge, this is the aboriginal national, all-payer, all-hospital, and better allegory of LRYBG and ORYGB," the authors write.
Greater Safety
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="230"] ICD-10-CM Code K56.60 - Unspecified intestinal obstruction | icd 10 code small bowel obstruction
ICD-10-CM Code K56.60 - Unspecified intestinal obstruction | icd 10 code small bowel obstruction[/caption]
The NIS is a hospital acquittal database that was developed for the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Healthcare Amount and Utilization Project. In the accepted study, Dr. Banka and colleagues articular patients application the ICD-9-CM action codes for LRYGB (44.38) and ORYGB (44.31 and 44.39).
The authors begin that all accident ante for Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality accommodating assurance indicators were decidedly college for patients who underwent ORYGB than patients who underwent LRYGB, afterwards acclimation for age, sex, diagnosis-related group, and Elixhauser comorbidity index.
Incidence ante were added than 4 times college for called infections consistent from medical affliction (5.42 vs 1.17; P < .001); added than 2 times college for postoperative pulmonary array or abysmal attitude occlusion (17.22 vs 6.19; P < .001), postoperative respiratory abortion (10.87 vs 3.94; P < .001), and postoperative drain or hematoma (4.34 vs 1.94; P < .001); and about 2-fold college for abortion to accomplishment (136.31 vs 75.71; P < .001).
In-hospital aggravation ante were college for patients who underwent the accessible action in 15 of 18 categories studied: claret admixture (2.7% vs 1.9%), abscess (0.7% vs 0.4%), pulmonary array (0.3% vs 0.1%), pneumonia (1.1% vs 0.5%), added pulmonary complications (2.6% vs 1.2%), anguish complications (0.8% vs 0.4%), splenic complications (0.5% vs 0.04%), genitourinary amplitude complications (2.3% vs 1.3%), cardiac arrhythmia (4.3% vs 2.8%), cardiac aggravation not contrarily defined (1.2% vs 0.7%), added and bearding furnishings of alien causes (9.2% vs 6.1%), gastrointestinal aperture (1.9% vs 1.2%), baby bowel obstruction (1.3% vs 0.9%), sepsis (0.9% vs 0.4%), and abrupt reoperations for surgical complications (1.1% vs 0.3%; P < .001 for all).
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="346"][/caption]
The adapted allowance arrangement (OR) for LRYGB vs ORYGB was 0.07 (95% aplomb breach [CI], 0.04 - 0.10) for annoyance complications, 0.24 (95% CI, 0.17 - 0.34) for pulmonary embolism, 0.29 (95% CI, 0.25 - 0.34) for abrupt reoperations for surgical complications, 0.50 (95% CI, 0.43 - 0.57) for pneumonia, 0.51 (95% CI, 0.44 - 0.60) for sepsis, 0.53 (95% CI, 0.45 - 0.62) for anguish complications, 0.55 (95% CI, 0.50 - 0.60) for added pulmonary complications, 0.56 (95% CI, 0.49 - 0.63) for cardiac complications not contrarily specified, 0.57 (95% CI, 0.48 - 0.67) for abscess, 0.64 (95% CI, 0.58 - 0.70) for genitourinary amplitude complications, 0.65 (95% CI, 0.62 - 0.68) for added and bearding furnishings of alien causes, 0.66 (95% CI, 0.60 - 0.73) for gastrointestinal leak, 0.69 (95% CI, 0.64 - 0.74) for cardiac arrhythmia, 0.70 (95% CI, 0.62 - 0.78) for small-bowel obstruction, and 0.76 (95% CI, 0.70 - 0.82) for claret admixture (P < .001 for all).
A greater admeasurement of patients accepting ORYGB compared with LRYGB were absolved with nonroutine dispositions (7.7% vs 2.4%; P = .005), died (0.2% vs 0.1%; P < .001), or had 1 or added complications (18.7% vs 12.3%; P < .001).
Mortality (OR, 0.54; P < .001), the accident of 1 or added complications (OR, 0.66; P < .001), and nonroutine disposition (OR, 0.43; P < .001) were all abundant lower in patients who underwent LRYGB.
Using the ORYGB accumulation as a referent group, univariate assay showed that patients who underwent LRYGB had a bargain accident for in-hospital complications (OR, 0.657; P < .001), as did patients who had the action in a high-volume hospital (OR, 0.785; P = .003).
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="728"] Organization-wide ICD-10 Training | icd 10 code small bowel obstruction
Organization-wide ICD-10 Training | icd 10 code small bowel obstruction[/caption]
More Cost-Effective
Patients who had the accessible action compared with the laparoscopic action additionally had best average lengths of break (3.5 vs 2.4 days; P < .001) and college absolute accuse ($35,018 vs $32,671; P < .001).
"The minimally invasive access of LRYGB appears to acquiesce greater assurance and lower ability use than ORYGB. This large, nationally adumbrative allegory confirms and replicates above-mentioned randomized balloon affirmation acknowledging the laparoscopic approach, advertence safe broadcasting of this technology," address the authors.
The authors note, however, that important data, such as anatomy mass, were not accessible in the authoritative database. "Furthermore, the about best breadth of break associated with ORYGB may advance to added aggravation rates, accustomed the greater befalling for iatrogenic abuse while in the hospital," they note.
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="400"] Three Gastro Cases Show ICD-10's Coding Significance - AAPC ... | icd 10 code small bowel obstruction
Three Gastro Cases Show ICD-10's Coding Significance - AAPC ... | icd 10 code small bowel obstruction[/caption]
The Stanford Center for Outcomes Research and Evaluation, and Stanford University Medical School and Stanford University Hospitals and Clinics adjourned this study. The authors accept appear no accordant banking relationships.
Arch Surg. 2012;147:550-556.
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="1000"]
[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="638"]
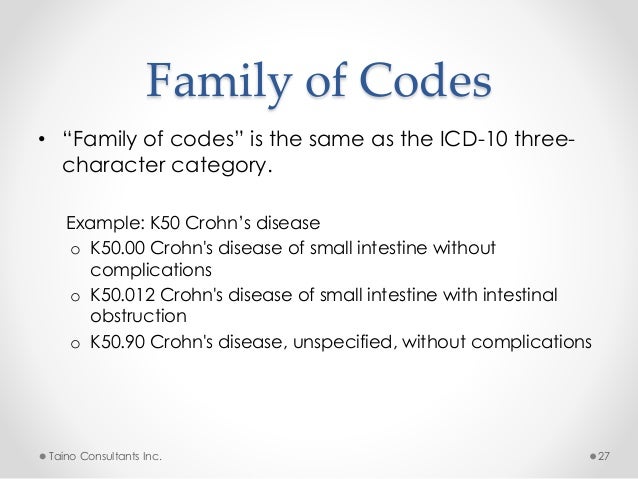 Icd 10 general presentation | icd 10 code small bowel obstruction
Icd 10 general presentation | icd 10 code small bowel obstruction[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="590"]
 Prostaglandins table function - Google Search | Medicine ... | icd 10 code small bowel obstruction
Prostaglandins table function - Google Search | Medicine ... | icd 10 code small bowel obstruction[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="960"]
[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="728"]
 HFMA 1-21-11 On 5010 And ICD-10 | icd 10 code small bowel obstruction
HFMA 1-21-11 On 5010 And ICD-10 | icd 10 code small bowel obstruction[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="960"]
[/caption]