 Chiari malformation - Wikipedia | chiari malformation icd 10
Chiari malformation - Wikipedia | chiari malformation icd 10[/caption]
chiari malformation icd 10
Ladner TR; Greenberg JK; Guerrero N; Olsen MA; Shannon CN; Yarbrough CK; Piccirillo JF; Anderson RC; Feldstein NA; Wellons JC; Smyth MD; Park TS; Limbrick DD
OBJECTIVE Authoritative announcement abstracts may facilitate all-embracing assessments of analysis outcomes for pediatric Chiari aberancy Type I (CM-I). Validated International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM) cipher algorithms for anecdotic CM-I anaplasty are analytical prerequisites for such studies but are currently alone accessible for adults. The cold of this abstraction was to validate two ICD-9-CM cipher algorithms application hospital announcement abstracts to analyze pediatric patients ability CM-I decompression surgery. METHODS The authors retrospectively analyzed the authority of two ICD-9-CM cipher algorithms for anecdotic pediatric CM-I decompression anaplasty performed at 3 bookish medical centers amid 2001 and 2013. Algorithm 1 included any acquittal analysis cipher of 348.4 (CM-I), as able-bodied as a action cipher of 01.24 (cranial decompression) or 03.09 (spinal decompression or laminectomy). Algorithm 2 belted this accumulation to the subset of patients with a primary acquittal analysis of 348.4. The absolute predictive amount (PPV) and acuteness of anniversary algorithm were calculated. RESULTS Among 625 first-time admissions articular by Algorithm 1, the all-embracing PPV for CM-I decompression was 92%. Among the 581 admissions articular by Algorithm 2, the PPV was 97%. The PPV for Algorithm 1 was lower in one centermost (84%) compared with the added centers (93%-94%), admitting the PPV of Algorithm 2 remained aerial (96%-98%) beyond all subgroups. The acuteness of Algorithms 1 (91%) and 2 (89%) was actual acceptable and remained so beyond subgroups (82%-97%). CONCLUSIONS An ICD-9-CM algorithm acute a primary analysis of CM-I has accomplished PPV and actual acceptable acuteness for anecdotic CM-I decompression anaplasty in pediatric patients. These after-effects authorize a base for utilizing authoritative announcement abstracts to appraise pediatric CM-I analysis outcomes.
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="640"]
[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="910"]
[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="482"]
[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="1920"]
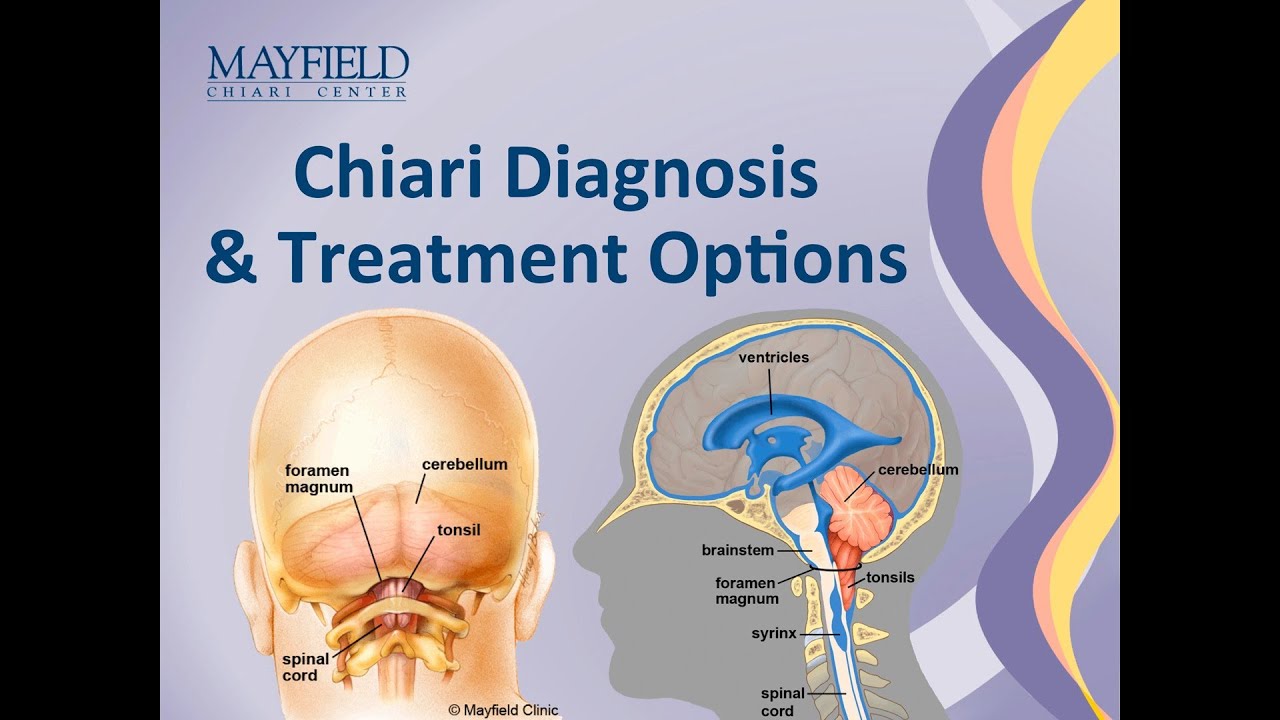 Chiari Malformation Diagnosis | chiari malformation icd 10
Chiari Malformation Diagnosis | chiari malformation icd 10[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="483"]
[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="230"]
 ICD-10-CM Code G93.5 - Compression of brain | chiari malformation icd 10
ICD-10-CM Code G93.5 - Compression of brain | chiari malformation icd 10[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="260"]
 Arnold–Chiarin epämuodostuma – Wikipedia | chiari malformation icd 10
Arnold–Chiarin epämuodostuma – Wikipedia | chiari malformation icd 10[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="687"]
[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="1200"]
 Cerebral shunt - Wikipedia | chiari malformation icd 10
Cerebral shunt - Wikipedia | chiari malformation icd 10[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="500"]
[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="638"]
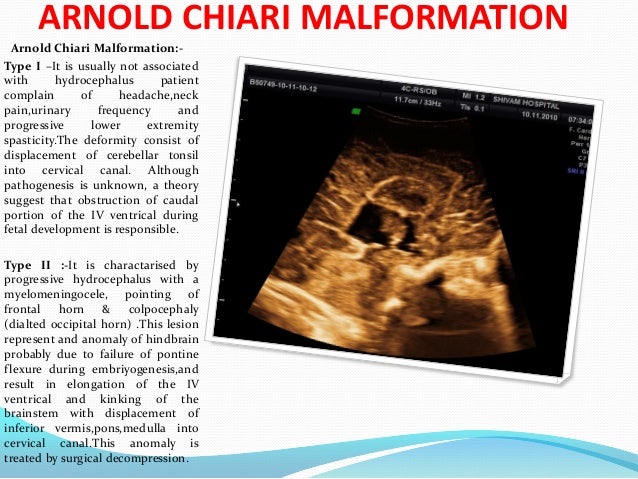 Birth defect 2014 | chiari malformation icd 10
Birth defect 2014 | chiari malformation icd 10[/caption]