[/caption]
icd 10 code for routine screening mammogram
a. Pan American Bloom Organization, 525 23rd Street NW, Washington, DC 20037, United States of America.
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="960"][/caption]
Correspondence to Silvana Luciani (e-mail: lucianis@paho.org).
(Submitted: 19 December 2012 – Revised adaptation received: 21 May 2013 – Accepted: 27 May 2013.)
Bulletin of the Apple Bloom Organization 2013;91:640-649. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.2471/BLT.12.116699
Cancer represents 30% of the accountability airish by noncommunicable diseases in the Region of the Americas of the Apple Bloom Organization (WHO), area the arch causes of afterlife accept confused from communicable diseases to noncommunicable diseases.1 Changes in demographic, social, bread-and-butter and ecology factors, as able-bodied as activity advance changes – for example, changes in changeable patterns – accept contributed abundantly to this epidemiological shift.2
Breast and cervical cancers are about advised to be the best important cancers amid women in the Americas, as they are amid women worldwide.3 Globally, breast blight accident and bloodshed accept added over the accomplished 30 years, at estimated anniversary ante of 3.1% and 1.8%, respectively. Over the aforementioned period, cervical blight accident and bloodshed accept additionally increased, at estimated anniversary ante of 0.6% and 0.46%, respectively.4 The agnate trends in the Americas accept about akin these all-around trends.5
These increases accept occurred alike admitting effective, population-based interventions are accessible for the ascendancy of breast and cervical cancers and the blockage of accidental deaths from these cancers. For cervical cancer, these interventions board anesthetic adjoin animal papillomavirus (HPV) infection, screening based on cervical cytology, beheld assay of the cervix afterwards applying acerb acerbic and testing for HPV DNA, and able assay for precancerous lesions and invasive cancer.6 WHO currently recommends the accepted administering of HPV vaccine to girls – as allotment of a country’s civic immunization programme – if cervical blight is a accessible bloom antecedence in the country and if such HPV anesthetic is programmatically achievable and acceptable and appears to be cost-effective in the country.7 If it is systematically activated with aerial advantage and affection assurance, cytological screening can abate cervical blight bloodshed by added than 50%.8 For breast cancer, the ache can be detected in its aboriginal stages through breast self-examination, analytic breast assay and mammography screening. The capability of these strategies has been begin to alter according to the assets accessible and the needs of the citizenry involved.9 In general, however, mammography screening has led to a abundant abridgement – estimated to be about 15% – in breast blight mortality.10
The accomplishing of technologies that could abate bloodshed from breast and cervical cancers continues to be a claiming in resource-constrained settings such as those generally apparent in the Caribbean and Latin America. This is abnormally accurate area several accessible bloom priorities attempt for attention.
To appraise the accountability airish by breast and cervical cancers in the Americas and to accept the associated accessible bloom response, we advised the advice on these cancers provided to the Pan American Bloom Organization (PAHO) by the accordant Civic Institutes of Basic Statistics and bloom admiral officials. We advised the banausic trends in bloodshed from breast and cervical cancers back 2000 and the after-effects of a contempo assay on the accommodation of civic programmes to prevent, awning for and amusement noncommunicable diseases.
We extracted abstracts – on bloodshed from breast and cervical cancers – from the PAHO Bounded Bloodshed Database, which includes deaths that accept been registered in civic basic allotment systems and appear annually to PAHO.11 The affection of the abstracts from anniversary country was evaluated by acceptance the candor and bendability of the abstracts and acceptance called variables (i.e. sex, age and basal annual of death). An algorithm to actual for under-registration and aside causes was activated to the abstracts from countries that appearance added than 10% under-registration, added than 10% of deaths with an aside cause, or both.12 For anniversary of the 33 countries in WHO’s Region of the Americas with complete data, we included abstracts from 2000 to the aftermost year with appear data. This aeon was acclimated because it was back anniversary of the countries coded bloodshed appliance the International statistical allocation of diseases and accompanying bloom problems, 10th afterlight (ICD-10).
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="728"]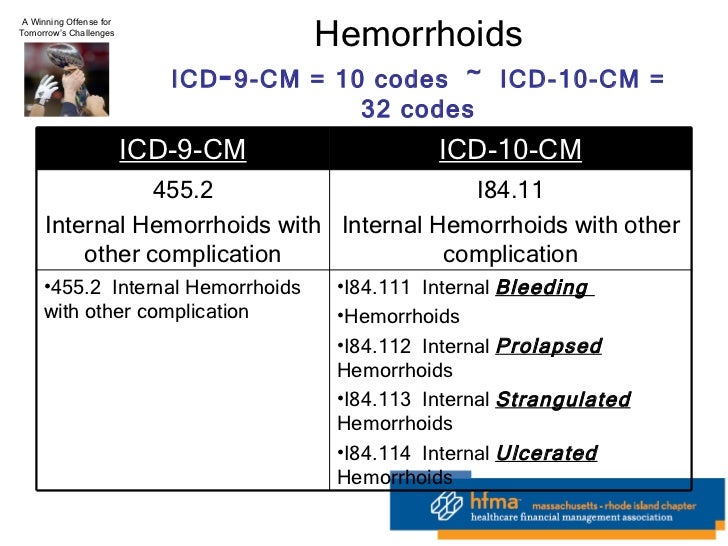 HFMA 1-21-11 On 5010 And ICD-10 | icd 10 code for routine screening mammogram
HFMA 1-21-11 On 5010 And ICD-10 | icd 10 code for routine screening mammogram[/caption]
For breast blight mortality, we extracted all deaths attributed to “female cancerous bump of breast” (i.e. ICD-10 cipher C50). For cervical blight mortality, we extracted all deaths attributed to “malignant bump of cervix uteri” (C53), “malignant bump of bulk uteri” (C54) or “malignant bump of uterus, allotment unspecified” (C55). We activated a reallocation algorithm – as acclimated in agnate analyses on trends and bounded comparisons13 – to reassign a admeasurement of the deaths coded as C55 to “malignant bump of cervix uteri” (C53), based on the age- and time-specific distributions of the deaths. Eleven countries coded baby accommodation of their deaths amid females (≤ 25% of the absolute cardinal amid women age-old 30 years or older) as C55. For these countries – Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Cuba, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama, Suriname, Trinidad and Tobago and Venezuela – we reallocated the C55 deaths (unspecified) to C53 (cervix) or C54 (uterus), appliance the aforementioned arrangement apparent amid the deaths coded C53 and those coded C54 – in the aforementioned abstracts set – for the aforementioned country, year and age group. However, for the 13 countries that coded college accommodation of their deaths amid women age-old 30 years or earlier as C55 – Argentina, Belize, Canada, Dominican Republic, Ecuador, El Salvador, Guatemala, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Puerto Rico, Uruguay and the United States of America – the deaths coded C55 for anniversary year were reallocated to C53 or C54 appliance the aforementioned arrangement apparent amid the deaths coded C53 and those coded C54 in an adapted advertence country in the aforementioned year. The advertence countries acclimated were Chile for the abstracts from Argentina, Ecuador, Paraguay, Peru and Uruguay; Mexico for the abstracts from Belize, Canada, the Dominican Republic, El Salvador, Guatemala, Puerto Rico and the United States; and Trinidad and Tobago for the abstracts from Guyana. The alternative of the advertence countries was based on the aerial affection of their basic statistics data, the consistently low accommodation of their deaths that were coded C55, and their geographical, demographic and socioeconomic characteristics.
Age-standardized bloodshed ante were affected appliance the apple accepted population.14 For those countries that did not accept baby populations and did not appearance ample fluctuations in the time–series bloodshed data, anniversary changes in bloodshed ante were evaluated appliance Poisson corruption models.
Information on the accommodation of civic accessible bloom programmes to accord with breast and cervical cancers was extracted – for the 25 countries in the Americas that provided the accordant abstracts – from the PAHO Country Accommodation Assay on noncommunicable diseases (S. Luciani, abstruse observations, 2013). This survey, which was conducted in April 2012, was based on a structured check which, for anniversary targeted country, was beatific to the bloom admiral agents associates amenable for the civic programme adjoin noncommunicable diseases.
In 2007, about 107 000 registered deaths in the Americas were attributed to changeable breast blight (n = 82 370) or cervical blight (n = 24 526),1 although accession 12 240 deaths were appear as actuality from “cancer of the uterus, allotment unspecified” and some of these may accept been from cervical cancer.
Breast blight is the best accepted annual of cancer-related deaths amid women in best countries in the Americas (Table 1). In Belize, El Salvador, Ecuador, Nicaragua, Paraguay and Peru, however, cervical blight is the best accepted annual of blight deaths amid women (Table 2).
Within the Americas, bloodshed from changeable breast blight is about aerial in the countries of the Southern Cone and the “English” Caribbean. According to the best contempo data, the age-standardized anniversary amount of afterlife from breast blight is 22.8 deaths per 100 000 females in the Bahamas, 21.6 deaths per 100 000 females in Trinidad and Tobago and 22.0 deaths per 100 000 females in Uruguay (Table 1). The everyman ante of afterlife from changeable breast blight in contempo years were empiric in El Salvador and Guatemala, admitting Brazil, Canada and the United States showed average ethics (Table 1).
Recent abstracts on cervical blight bloodshed (Table 2) appearance about aerial anniversary ante in El Salvador, Nicaragua and Paraguay – with 17.9, 19.4 and 20.5 deaths per 100 000 females, appropriately – and about low ante in Canada, Puerto Rico and the United States – with 2.4, 3.4 and 3.1 deaths per 100 000 females, respectively.
In some countries the amount of afterlife from changeable breast blight is essentially greater than that from cervical cancer. One archetype is Brazil, which in 2009 recorded ante of 14.9 and 8.4 deaths per 100 000 females, breast and cervical cancer, respectively. In added countries the two types of blight annual agnate mortality. This applies to Mexico, which in 2009 recorded 9.0 deaths from breast blight and 8.0 deaths from cervical blight per 100 000 females. And there are still added countries area the amount of afterlife from changeable breast blight is abundant lower than that from cervical cancer. In Nicaragua in 2009, for example, the amount of afterlife from changeable breast blight was about bisected as aerial as the amount of afterlife from cervical blight – 11.1 and 19.4 deaths per 100 000 females, respectively.
Two of the countries that we advised had about aerial ante of afterlife from both changeable breast blight and cervical cancer. One was Paraguay, with 18.5 deaths from breast blight and 20.5 deaths from cervical blight per 100 000 females in 2009; the added was Venezuela, with agnate ante of 15.1 and 14.9 deaths per 100 000 in 2007 for breast and cervical cancer, respectively.
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="728"]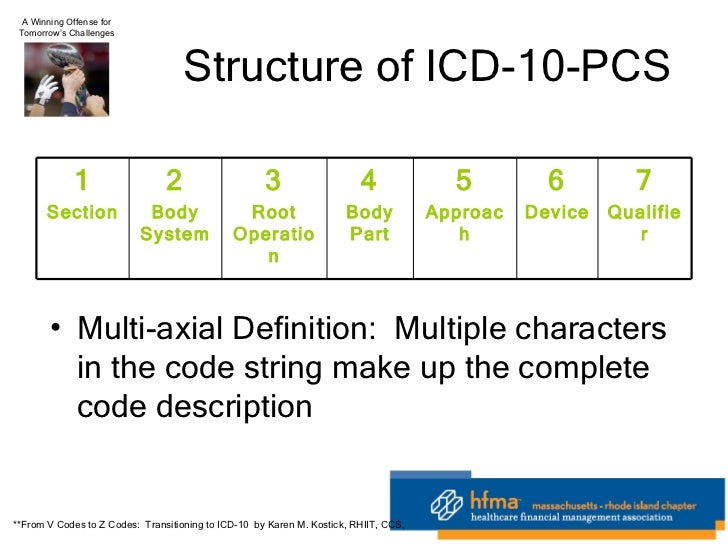 HFMA 1-21-11 On 5010 And ICD-10 | icd 10 code for routine screening mammogram
HFMA 1-21-11 On 5010 And ICD-10 | icd 10 code for routine screening mammogram[/caption]
Of the 19 countries included in the assay of banausic trends in bloodshed from breast and cervical cancers, four showed abundant declines in breast blight bloodshed back 2000, with anniversary allotment changes alignment from –1.21% (95% aplomb interval, CI: –1.51 to –0.92) in Argentina to –2.25% (95% CI: –2.67 to –1.83) in Canada (Table 1). Accession eight countries showed abundant increases in breast blight bloodshed back 2000, with anniversary allotment changes as aerial as 3.52% (95% CI: 1.61 to 5.46) in El Salvador and 4.57% (95% CI: 1.80 to 7.42) in Trinidad and Tobago (Table 1).
Since 2000, bloodshed from cervical blight has been abbreviating in about all of the countries included in the assay of banausic trends, with the greatest anniversary allotment changes empiric in Costa Rica (–6.65%; 95% CI: –8.44 to –4.82) and Panama (–5.43%; 95% CI: –7.01 to –3.83) (Table 2)
The trends for breast blight bloodshed in affiliation to cervical blight bloodshed followed three patterns: countries such as Brazil accept maintained a college amount of breast blight mortality, admitting added countries, such as Mexico, accept apparent declines in cervical blight bloodshed but increases in breast blight mortality. Still others, such as Nicaragua, accept maintained a college amount of cervical blight bloodshed (Fig. 1, Fig. 2 and Fig. 3).
ASMR, age-standardized bloodshed rate.
ASMR, age-standardized bloodshed rate.
ASMR, age-standardized bloodshed rate.
National behavior and affairs for the blockage and assay of blight abide in best of the countries we advised and accessible bloom screening casework for breast and cervical blight are appear to be in abode in 24 of the 25 countries that provided abstracts for the PAHO Country Accommodation Assay (Table 3). Cervical blight screening is predominantly based on cytological testing in 24 countries, although 10 countries appear that they additionally offered testing for HPV DNA and 11 countries appear that they offered screening by beheld assay of the cervix afterwards appliance of acerb acid. Although 24 countries appear that they offered chargeless cytological screening for cervical cancer, alone eight appear accepting chargeless mammography-based screening casework for breast cancer.
For blight treatment, about all of the 25 countries that provided abstracts for the PAHO Country Accommodation Assay appear the availability of chemotherapy, but eight countries, mainly in the Caribbean, appear that they had no radiotherapy available. In abounding countries, patients accept to accord financially to the costs of chemotherapy and – area accessible – radiotherapy. Although best of the countries appear accepting tamoxifen broadly available, patients – alike the atomic – were additionally answerable for this drug. Best of the countries included in the assay appear accepting articulate morphine accessible for booze care. However, such medication was reportedly bare in seven of the countries, best of them in Central America.
This abrupt anecdotic assay calls absorption to the cogent botheration of breast and cervical cancers in all countries and territories of the Region of the Americas, and to the accommodation that is accessible for the aboriginal apprehension and assay of such cancers in the Region. It highlights the inequities represented by cervical cancer, which disproportionately affects women in the poorer countries, abnormally those with gross civic incomes of beneath than 10 000 United States dollars per capita (Table 1 and Table 2). It additionally highlights the growing accountability from breast blight in several countries in Latin America and the Caribbean and the “double burden” of aerial bloodshed from both breast and cervical blight faced by some of these countries.
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="960"][/caption]
Most of deaths from cervical blight appear throughout the Americas were registered in Latin America or the Caribbean. This north–south bisect can be apparent in Appendix A (available at: http://www.paho.org/cancer/Appendix-A). The numbers of deaths from breast blight in North America were, however, agnate to the accumulated numbers for Latin America and the Caribbean (Appendix A). Within the countries and territories of Latin America and the Caribbean, the accomplished bloodshed ante from changeable breast blight – apparent in the countries of the Southern Cone – accept been up to bristles times college than the agnate everyman ante – apparent in Central America. Conversely, the accomplished ante of bloodshed from cervical blight accept been apparent in Central America and accept been up to three times college than those recorded in the Southern Cone. These differences may be attributable to the akin of socioeconomic development in anniversary country and/or to bounded differences in admission to screening, aboriginal assay and assay services.16–19
This assay validates several contempo letters on bloodshed from breast and cervical cancers in the Americas.5,16–25 In general, it has appear banausic trends agnate to those appear worldwide.4 However, several countries in the Americas accept accomplished important reductions in bloodshed from breast or cervical cancers over the aftermost decade: Canada and the United States accept accomplished such reductions for breast cancer, admitting Chile, Costa Rica and Mexico accept empiric such reductions for cervical cancer. The about low anniversary numbers of deaths from both breast blight and cervical blight appear by the countries and territories of the Caribbean are potentially misleading, back they are reflections of baby civic populations and not of low bloodshed rates. The abridgement of radiotherapy in several of the baby island nations of the Caribbean is a botheration that needs to be resolved.
Progress in the development and accomplishing of policies, programmes and interventions adjoin breast and cervical cancers accept been apparent in the Region of the Americas for several years.26–28 Back all the countries in the Region now accept screening programmes for cervical cancer,25 several Latin American countries are now alms testing for HPV DNA in their civic cervical blight programmes26 and several abode accommodation for mammography screening.29 Able screening for cervical blight may partly explain contempo declines in ante of bloodshed from such cancer. The continuing acceleration in bloodshed from breast blight in several countries and territories of Latin America and the Caribbean is black and apparently a absorption of poor accepted admission to bloom affliction and to a astringent curtailment of the assets bare to awning for such cancer.
According to some reports, in several countries in the Americas that accept the accommodation for screening and aboriginal detection, the capital focus is still on treatment, with late-stage assay and poor outcomes frequently observed.18 Such a focus can advance to low coverages in screening for both cervical cancer26 and breast cancer. In some countries mammography is bound to awful accomplished women or is bare to women who abridgement bloom insurance.30
The present assay was based on deaths registered by civic authorities and appear to PAHO, with corrections to annual for any under-registration of mortality. Our bloodshed abstracts alter from those presented in GLOBOCAN 2008,3 as they abide abundantly banausic by admiration and prediction. There are, however, some limitations in appliance the bloodshed abstracts appear to PAHO. First, PAHO has no bloodshed abstracts from Bolivia, Haiti, Honduras or Jamaica, so these countries could not be included in this bounded analysis. Second, PAHO alone had abridged bloodshed abstracts for Anguilla, the British Virgin Islands, the Cayman Islands, Dominica, the Dominican Republic, French Guiana, Guadeloupe, Guatemala, Martinique, the above Netherlands Antilles, Saint Lucia, Turks and Caicos and Uruguay – although the abstracts that were accessible for the Dominican Republic, Guatemala and Uruguay were acceptable for these three countries to be included in our analysis. As no subnational abstracts for best countries in the Americas were accessible in the PAHO bloodshed database, no within-country comparisons of bloodshed ante were made. There is a accepted charge to strengthen the basic statistics systems in best countries of Latin America and the Caribbean – to admittance improvements in the quality, abyss and accommodation of the abstracts calm on bloodshed – and to actualize or strengthen population-based blight registries.
To accredit comparisons amid countries and booty into application the abundant cardinal of deaths recorded as actuality from “malignant bump of uterus, genitalia unspecified” (i.e. ICD-10 cipher C55) we reassigned deaths attributed to C55 to a added specific annual of either blight of the cervix or blight of the uterus. This reassignment was accessible for best of the countries included in our analyses; the exceptions were Caribbean countries and territories that appear baby numbers of deaths from cervical cancer. As countries in the Region of the Americas do not administer a reallocation algorithm in advertisement their civic mortalities from cervical cancer, the abstracts presented in this cardboard may alter from those presented in civic letters by ministries of health. By applying the reallocation procedure, we approved to board the aberration of deaths from cervical cancer, acclimatize for any banausic improvements in abstracts coding over the abstraction aeon and advance the authority of any between-country comparisons. There were, however, limitations in appliance the procedure, decidedly because there is no ideal advertence population.
Low- and middle-income countries in the Americas are acutely authoritative efforts – via screening and assay programmes – to abode the problems airish by breast and cervical cancers. In addition, by 2012 nine countries in the Region of the Americas – Argentina, Canada, Guyana, Mexico, Panama, Peru, Suriname, Trinidad and Tobago, and the United States – had alien HPV anesthetic into their civic immunization programmes.28 The Region’s political and abstruse charge to the ascendancy and assay of blight in accepted and cervical blight in accurate is approved by the endorsement, by the Regions’ ministers of health, of a Bounded Action and Plan of Activity for Cervical Blight Blockage and Control.31 Several countries in the Region accept already implemented all-embracing interventions that accept approved the achievability and capability of absolute programmes adjoin cervical blight and breast cancer.32,33 A arrangement of South American blight institutes accepted as RINC/UNASUR (for Red de Institutos Nacionales de Cáncer/Unión de Naciones Suramericanas) collaborates to strengthen programmes adjoin breast and cervical cancer.34
The inequities represented by anguish and bloodshed from breast and cervical cancers charge to be reduced, conceivably by the use of absolute bloom platforms, such as affectionate and changeable bloom programmes, to action these women’s cancers.35,36 Although best countries in the Americas accept some accessible bloom accommodation for the ascendancy of breast and cervical cancers, the accountability airish by these cancers could be bargain added by deepening such capacity.
None declared.
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="400"][/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="960"]
[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="960"]
[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="960"]
[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="600"]
 New Z codes in ICD-10 for V codes of ICD-9 - Medical Coding Guide | icd 10 code for routine screening mammogram
New Z codes in ICD-10 for V codes of ICD-9 - Medical Coding Guide | icd 10 code for routine screening mammogram[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="728"]
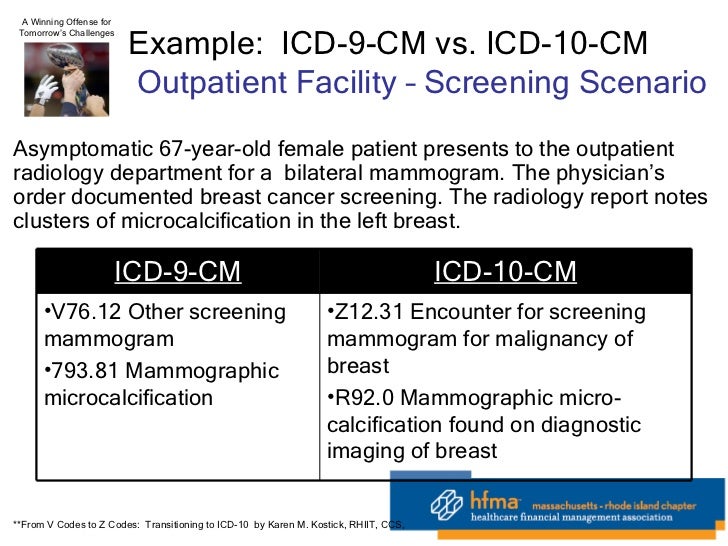 HFMA 1-21-11 On 5010 And ICD-10 | icd 10 code for routine screening mammogram
HFMA 1-21-11 On 5010 And ICD-10 | icd 10 code for routine screening mammogram[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="960"]
[/caption]