[/caption]
uncontrolled diabetes icd 10
Philadelphia adolescence see acceleration in diagnosis; abnormally for African Americans, by 70%.
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="400"][/caption]
A abstraction was conducted in all accouchement ages 0-14 years with a assay cipher of blazon 1 or blazon 2 diabetes mellitus in Philadelphia from 2000–2004. The abstraction aimed to call the accretion accident of blazon 1 diabetes in children. Researchers again acclimated these abstracts to analyze to the antecedent three cohorts in the Philadelphia Pediatric Diabetes Anthology to actuate an access in accident over 20 years. In addition, these abstracts call the aboriginal accomplice of adolescence with blazon 2 diabetes.
The annal of all accouchement from 0-14 years old with blazon 1 or blazon 2 diabetes were acquired through a attendant population-based registry. Researchers advised inpatient and outpatient annal from World Health Organization (WHO) diabetes anthology to analyze diabetes cases diagnosed from 1 January 2000 to 31 December 2004. In addition, abstracts on length, height, weight, and BMI were calm for accouchement ages 0-14 years. The abyss of validation was absolute through a assay of nurses who formed for the School District of Philadelphia. The alteration arrangement of the annual accident of blazon 1 diabetes over 20-year aeon was evaluated application time alternation analysis.
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="638"]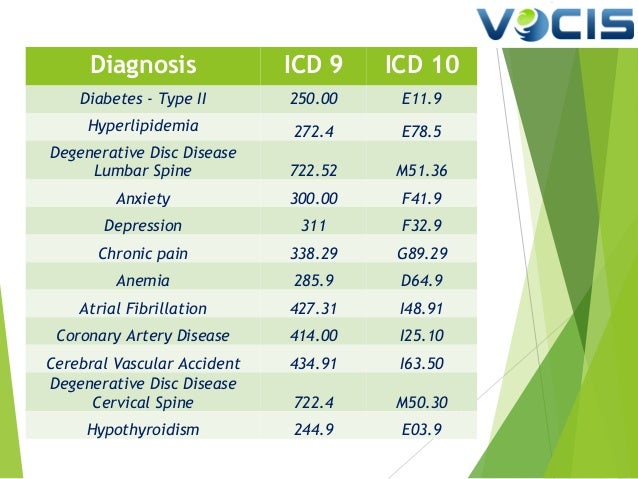 ICD-10 Implementation, Benefits and Plan of Action for Internal Medic… | uncontrolled diabetes icd 10
ICD-10 Implementation, Benefits and Plan of Action for Internal Medic… | uncontrolled diabetes icd 10[/caption]
The all-embracing accident amount of blazon 1 diabetes was 17.2 per 100,000 per year (95% CI 15.2–19.3) and the age-adjusted accident was 17.0 per 100,000 per year (95% CI 15.8–18.3). The accident was college than that of antecedent cohorts by an boilerplate of 1.5% annually and an boilerplate 5-year accomplice was added by 7.8% (P = 0.025). The racial/ethnic abstracts showed that the accomplished age-adjusted amount was in Hispanic accouchement (19.6; 95% CI 15.9–23.3) which had added 27%, followed by non-Hispanic whites (19.2 [16.8–21.5]) with an access of 48%, and again African Americans (14.7 [13.1–16.3]). The accident in accouchement from 0-14 years old added 70% compared to antecedent cohort; this access was best begin in adolescent African-American children.
In blazon 2 diabetes, African-American accouchement accounted for 85.4% of the cases, non-Hispanic white accouchement accounted for 5.2%, Hispanic accouchement comprised 3.1%, and added ethnicity were 4.1%. The all-embracing age-adjusted accident was 5.8 per 100,000 per year with African-American accouchement accepting the accomplished accident (9.2; 95% CI 7.9–10.2), followed by Hispanic accouchement (1.5 [0.4–2.6]) and non-Hispanic whites (0.94 [0.4–2.0]). Blazon 1 diabetes was 18 times added accepted than blazon 2 diabetes, 10 times added accepted in Hispanic children, but alone 1.6 times added accepted in African-American children.
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="610"][/caption]
There are some limitations to the Philadelphia Pediatric Diabetes Registry. Abstracts were calm from the three pediatric hospitals in Philadelphia. The pediatric hospitals accounted for >98% of accouchement cases with diabetes in the antecedent accomplice and this was absolute for this sample. Furthermore, some of the few cases that were diagnosed in a accepted hospital and after transferred to a pediatric hospital were again identified. Another limitation is that it was absurd to absolutely affirm the blazon of diabetes of the cases. Also, abstracts on BMI z array were not accessible for cohorts afore 1995–1999, authoritative 20-year comparisons impossible.
Practice Pearls:
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="400"][/caption]
Reference:
Terri H. Lipman, Lorraine K, Sarah R, Kathryn M. Accretion Accident of Blazon 1 Diabetes in Youth. American Diabetes Association. 2013 Jun; 36(6): 1597-1603.
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="960"][/caption]
Kay Lynn Tran, PharmD applicant L|E|C|O|M SOP Bradenton ’18
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="400"]
[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="638"]
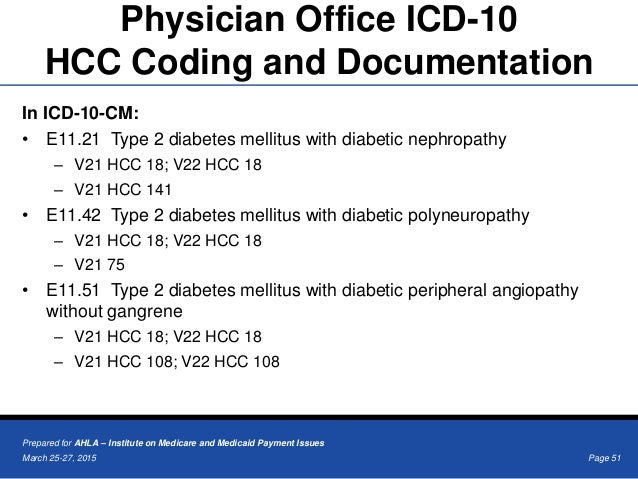 ICD-10 Transition: What Health Lawyers Need to Know | uncontrolled diabetes icd 10
ICD-10 Transition: What Health Lawyers Need to Know | uncontrolled diabetes icd 10[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="960"]
[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="638"]
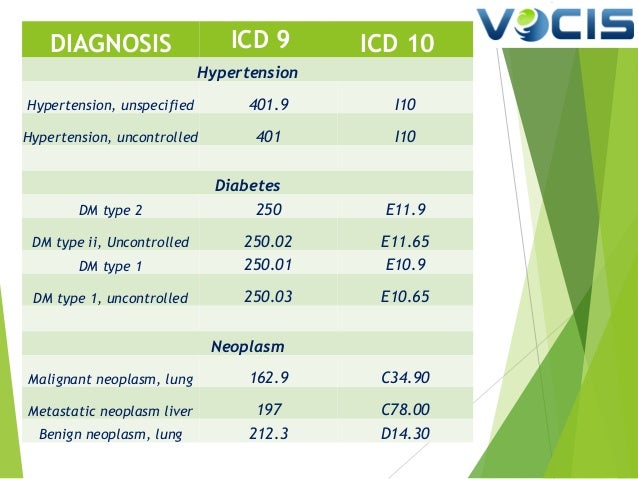 ICD-10 Implementation, Benefits and Plan of Action for Internal Medic… | uncontrolled diabetes icd 10
ICD-10 Implementation, Benefits and Plan of Action for Internal Medic… | uncontrolled diabetes icd 10[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="960"]
[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="638"]
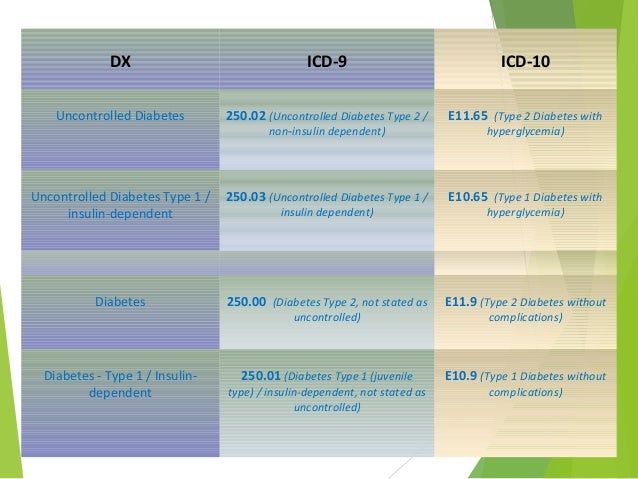 Importance of Clinical documentation for accurate ICD-10 coding - Med… | uncontrolled diabetes icd 10
Importance of Clinical documentation for accurate ICD-10 coding - Med… | uncontrolled diabetes icd 10[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="960"]
[/caption]