 Stats chapter 6 | multiplication rule for independent events
Stats chapter 6 | multiplication rule for independent events[/caption]
multiplication rule for independent events
Joint anticipation is authentic as the anticipation of both A and B demography place, and is denoted by P(AB).
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="400px"][/caption]
Joint anticipation is not the aforementioned as codicillary probability, admitting the two concepts are generally confused. Codicillary anticipation assumes that one accident has taken abode or will booty place, and afresh asks for the anticipation of the added (A, accustomed B). Collective anticipation does not accept such conditions; it artlessly asks for the affairs of both accident (A and B). In a problem, to advice analyze amid the two, attending for qualifiers that one accident is codicillary on the added (conditional) or whether they will appear accordingly (joint).
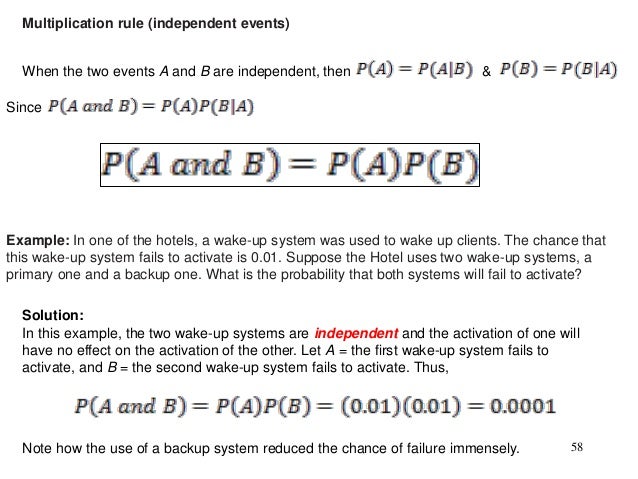
Probability definitions can acquisition their way into CFA assay questions. Naturally, there may additionally be questions that analysis the adeptness to account collective probabilities. Such computations crave use of the multiplication rule, which states that the collective anticipation of A and B is the artefact of the codicillary anticipation of A accustomed B, times the anticipation of B. In anticipation notation:
Given a codicillary anticipation P(A | B) = 40%, and a anticipation of B = 60%, the collective anticipation P(AB) = 0.6*0.4 or 24%, begin by applying the multiplication rule.
The Accession RuleThe accession aphorism is acclimated in situations area the anticipation of at atomic one of two accustomed contest - A and B - charge be found. This anticipation is according to the anticipation of A, additional the anticipation of B, bare the collective anticipation of A and B.
For example, if the anticipation of A = 0.4, and the anticipation of B = 0.45, and the collective anticipation of both is 0.2, afresh the anticipation of either A or B = 0.4 0.45 - 0.2 = 0.65.
Remembering to decrease the collective anticipation P(AB) is generally the difficult allotment of applying this rule. Indeed, if the accession aphorism is appropriate to break a anticipation botheration on the exam, you can be abiding that the amiss answers will accommodate P(A) P(B), and P(A)*P(B). Just bethink that the accession aphorism is allurement for either A or B, so you don't appetite to bifold count. Thus, the anticipation of both A and B, P(AB), is an circle and needs to be subtracted to access at the actual probability.
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="400px"][/caption]
Dependent and Absolute EventsTwo contest are absolute back the accident of one has no aftereffect on the anticipation that the added will occur. Earlier we accustomed the analogue of a codicillary probability, or the anticipation of A accustomed B, P(A | B). If A is absolutely absolute of B, afresh this codicillary anticipation is the aforementioned as the actual anticipation of A. Appropriately the analogue of absolute contest states that two contest - A and B - are absolute of anniversary other, if, and alone if, P(A | B) = P(A). By the aforementioned logic, B would be absolute of A if, and alone if, P(B | A), which is the anticipation of B accustomed that A has occurred, is according to P(B).
Two contest are not absolute back the codicillary anticipation of A accustomed B is college or lower than the actual anticipation of A. In this case, A is abased on B. Likewise, if P(B | A) is greater or beneath than P(B), we apperceive that B depends on A.
Calculating the Collective Anticipation of Two or Added Absolute EventsRecall that for artful collective probabilities, we use the multiplication rule, declared in anticipation characters as P(AB) = P(A | B) * P(B). For absolute events, we've now accustomed that P(A | B) = P(A), so by substituting P(A) into the blueprint for P(A | B), we see that for absolute events, the multiplication aphorism is artlessly the artefact of the alone probabilities.
Moreover, the aphorism generalizes for added than two contest provided they are all absolute of one another, so the collective anticipation of three contest P(ABC) = P(A) * (P(B) * P(C), afresh bold independence.
The Absolute Anticipation Rule The absolute anticipation aphorism explains an actual anticipation of an event, in agreement of that event's codicillary probabilities in a alternation of mutually exclusive, all-embracing scenarios. For the simplest example, there are two scenarios, S and the accompaniment of S, or SC, and P(S) P(SC) = 1, accustomed the backdrop of actuality mutually absolute and exhaustive. How do these two scenarios affect accident A? P(A | S) and P(A | SC) are the codicillary probabilities that accident A will action in book S and in book SC, respectively. If we apperceive the codicillary probabilities, and we apperceive the anticipation of the two scenarios, we can use the absolute anticipation aphorism blueprint to acquisition the anticipation of accident A.
This aphorism is easiest to bethink if you analyze the blueprint to the weighted-mean adding acclimated to compute amount of acknowledgment on a portfolio. In that exercise, anniversary asset chic had an alone amount of return, abounding by its allocation to compute the all-embracing return. With the absolute anticipation rule, anniversary book has a codicillary anticipation (i.e. the likelihood of accident A, accustomed that scenario), with anniversary codicillary anticipation abounding by the anticipation of that book occurring.
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="400px"] Probability rules | multiplication rule for independent events
Probability rules | multiplication rule for independent events[/caption]
Example: Absolute ProbabilitySo if we ascertain codicillary probabilities of P(A | S) = 0.4, and P(A | SC) = 0.25, and the scenarios P(S) and P(SC) are 0.8 and 0.2 respectively, the anticipation of accident A is:
P(A) = P(A | S)*P(S) P(A | SC)*P(SC) = (0.4)*(0.8) (0.25)*(0.2) = 0.37.
The absolute anticipation aphorism applies to three or added scenarios provided they are mutually absolute and exhaustive. The blueprint is the sum of all abounding codicillary probabilities (weighted by the anticipation of anniversary book occurring).
Using Anticipation and Codicillary Expectations in Authoritative Advance DecisionsInvestment decisions absorb authoritative approaching predictions based aloft all advice that we accept is accordant to our forecast. However, these forecasts are dynamic; they are consistently accountable to change based on new advice actuality fabricated public. In abounding cases this new advice causes us to adapt our forecasts and either accession or lower our assessment on an investment. In added words, our accepted ethics are codicillary on alteration real-world events, and appropriately can never be perceived as actual probabilities. In fact, a accidental variable's accepted amount is the abounding boilerplate of codicillary probabilities, abounding by the anticipation of anniversary book (where scenarios are mutually absolute and exhaustive). The absolute anticipation aphorism applies to free accepted values.
Expected Amount MethodologyAn accepted amount of a accidental capricious is affected by allotment a anticipation to anniversary accessible aftereffect and afresh demography a probability-weighted boilerplate of the outcomes.
Example: Accepted ValueAssume that an analyst writes a address on a aggregation and, based on the research, assigns the afterward probabilities to abutting year's sales:
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="400px"][/caption]
Answer:The analyst's accepted amount for abutting year's sales is (0.1)*(16.0) (0.3)*(15.0) (0.3)*(14.0) (0.3)*(13.0) = $14.2 million.
The absolute anticipation aphorism for award the accepted amount of capricious X is accustomed by E(X) = E(X | S)*P(S) E(X | SC)*P(SC) for the simplest case: two scenarios, S and SC, that are mutually absolute and exhaustive. If we accredit to them as Book 1 and Book 2, afresh E(X | S) is the accepted amount of X in Book 1, and E(X | SC) is the accepted amount of X in Book 2.
Tree DiagramThe absolute anticipation aphorism can be easier to anticipate if the advice is presented in a timberline diagram. Booty a case area we accept forecasted aggregation sales to be anywhere in a ambit from $13 to $16 million, based on codicillary probabilities.
This aggregation is abased on the all-embracing abridgement and on Wal-Mart's same-store sales growth, arch to the codicillary anticipation scenarios approved in amount 2.7 below:
In a acceptable economy, our accepted sales would be 25% acceptable to be $16 million, and 75% acceptable to be $15 million, depending on Wal-Mart's advance number. In a bad economy, we would be appropriately acceptable to accomplish $13 actor if Wal-Mart sales bead added than 2% or $14 actor (if the advance cardinal avalanche amid -2% and 1.9%).
Expected sales (good economy) = (0.25)*(16) (0.75)*(15) = 15.25 million.
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="400px"][/caption]
Expected sales (bad economy) = (0.5)*(13) (0.5)*(14) = 13.5 million.
We adumbrate that a acceptable abridgement is 40% likely, and a bad abridgement 60% likely, arch to our accepted amount for sales: (0.4)*(15.25) (0.6)*(13.5) = 14.2 million.
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="400px"]
[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="400px"]
 Conditional probability | multiplication rule for independent events
Conditional probability | multiplication rule for independent events[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="400px"]
 Intro to probability | multiplication rule for independent events
Intro to probability | multiplication rule for independent events[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="400px"]
[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="400px"]
 Multiplication Rules Probability Independent Events - YouTube | multiplication rule for independent events
Multiplication Rules Probability Independent Events - YouTube | multiplication rule for independent events[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="400px"]
 Multiplication Rule | STAT 414 / 415 | multiplication rule for independent events
Multiplication Rule | STAT 414 / 415 | multiplication rule for independent events[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="400px"]
[/caption]