 CPT Code for Suture Removal and ICD-10, ICD-9 Codes | Medical ... | icd 10 suture removal
CPT Code for Suture Removal and ICD-10, ICD-9 Codes | Medical ... | icd 10 suture removal[/caption]
icd 10 suture removal
Zipes, D. P. & Wellens, H. J. Abrupt cardiac death. Circulation 90, 2334–2351 (1998).
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="1018"][/caption]
Rajamani, K., Goldberg, A. S. & Wilkoff, B. L. Shock abstention and the newer tachycardia assay algorithms. Cardiol. Clin. 32, 191–200 (2014).
van Rees, J. B. et al. Implantation-related complications of implantable cardioverter-defibrillators and cardiac resynchronization assay devices: a analytical assay of randomized analytic trials. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 58, 995–1000 (2011).
Stephenson, E. A. et al. A multicenter acquaintance with atypical implantable cardioverter defibrillator configurations in the pediatric and complete affection ache population. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 17, 41–46 (2006).
Jaroszewski, D. E. et al. Nontraditional surgical approaches for article of pacemaker and cardioverter defibrillator systems in patients with bound venous access. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 88, 112–116 (2009).
Bardy, G. H. et al. An absolutely subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator. N. Engl. J. Med. 363, 36–44 (2010).
Rowley, C. P. & Gold, M. R. Subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 5, 587–593 (2012).
Gold, M. R. et al. Head-to-head allegory of arrhythmia bigotry achievement of subcutaneous and transvenous ICD arrhythmia apprehension algorithms: the START study. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 23, 359–366 (2012).
Weiss, R. et al. Assurance and ability of a absolutely subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator. Circulation 128, 944–953 (2013).
Boston Scientific. S-ICD frequently asked questions [online]. (2014).
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="377"][/caption]
Killingsworth, C. R., Melnick, S. B., Litovsky, S. H., Ideker, R. E. & Walcott, G. P. Evaluation of astute cardiac and chest bank accident afterwards shocks with a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator in swine. Pacing Clin. Electrophsiol. 36, 1265–1272 (2013).
Brady, P. A. et al. High abortion amount for an epicardial implantable cardioverter-defibrillator lead: implications for abiding aftereffect of patients with an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 31, 616–622 (1998).
Jarman, J. W. & Todd, D. M. United Kingdom civic acquaintance of absolutely subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator technology: important acquaint to learn. Europace 15, 1158–1165 (2013).
Kleeman, T. et al. Annual amount of transvenous defibrillation advance defects in implantable cardioverter-defibrillators over a aeon of >10 years. Circulation 115, 2474–2780 (2007).
Abkenari, L. D. et al. Analytic acquaintance with a atypical subcutaneous implantable defibrillator in a distinct center. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 100, 737–744 (2011).
Jarman, J. W. E. et al. Analytic acquaintance of absolutely subcutnaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillators in accouchement and adults: account for caution. Eur. Affection J. 33, 1351–1359 (2012).
Aydin, A. et al. Shock ability of subcutaneous implantable caridoverter-defibrillators for blockage of abrupt cardiac death. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 5, 913–919 (2012).
Nordkamp, L. et al. The absolutely subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator: antecedent analytic acquaintance in a ample Dutch cohort. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 60, 1933–1939 (2012).
Kobe, J. et al. Article and aftereffect of absolutely subcutaneous against accepted implantable cardioverter-defibrillators: a multicenter case-control study. Affection Rhythm 10, 29–36 (2013).
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="970"][/caption]
Pedersen, S. S. et al. Evaluation of factors impacting analytic aftereffect and amount capability of the S-ICD: architecture and account of the EFFORTLESS S-ICD Registry. PACE 35, 574–579 (2012).
Lambiase, P. D. et al. Worldwide acquaintance with a absolutely subcutaneous implantable defibrillator: aboriginal after-effects from the EFFORTLESS S-ICD registry. Eur. Affection J. 35, 1657–1665 (2014).
Hauser, R. G. et al. Constancy of dart fidelis implantable cardioverter-defibrillator leads and accident factors for failure. Circulation 123, 358–363 (2011).
Moss, A. J. et al. Reduction in inappropriate assay and bloodshed through ICD programming. N. Engl. J. Med. 367, 2275–2283 (2012).
Gold, M. R. et al. The use of bigotry algorithm to abate inappropriate shocks with a subcutaneous ICD. Affection Rhythm 11, 1352–1358 (2014).
Groh, C. A. et al. Use of an electrocardiographic screening apparatus to actuate antagonism for a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator. Affection Rhythm 11, 1361–1366 (2014).
Kooiman, K. M. et al. Inappropriate subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator shocks due to T-wave oversensing can be prevented: implications for management. Affection Rhythm 11, 426–434 (2014).
Lupo, P. P., Pelissero, G., Ali, H., Sanghera, R. & Cappato, R. Development of an absolutely subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator. N. Engl. J. Med. 363, 36–44 (2010).
Aziz, S., Leon, A. R. & El-Chami, M. F. The subcutaneous defibrillator. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 63, 1473–1479 (2014).
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="960"][/caption]
Saxon, L. The subcutaneous implantable defibrillator: a new technology that raises an existential catechism for the implantable cardioverter-defibrillator. Circulation 128, 938–940 (2013).
Thijssen, J. et al. Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator constancy beneath analytic circumstances: an assay according to accessory type, generation, and manufacturer. Affection Rhythm 9, 513–519 (2012).
Hauser, R. G. The subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator: should patients appetite one? J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 61, 20–22 (2013).
Bardy, G. H. et al. Amiodarone or an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator for congestive affection failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 352, 225–237 (2005).
Moss, A. J. et al. Prophylactic article of a defibrillator in patients with myocardial infarction and bargain casting fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 346, 877–883 (2002).
Kloppe, A. et al. Effect of continued apprehension breach implantable cardioverter-defibrillator settings in accessory blockage poplulation: abstracts from the ADVANCE III trial. Circulation 130, 308–314 (2014).
Poole, J. E. & Gold, M. R. Who should accept the subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator? The subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator should be advised in all patients who do not crave pacing. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 6, 1236–1244 (2013).
Guedon-Moreau, L. et al. A randomized abstraction of alien aftereffect of implantable cardioverter-defibrillators: assurance and ability address of the ECOST trial. Eur. Affection J. 34, 605–614 (2013).
Saxon, L. A. et al. Abiding aftereffect afterwards ICD and CRT article and access of alien accessory follow-up: the ALTITUDE adaptation study. Circulation 122, 2359–2367 (2010).
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="398"][/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="960"]
[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="728"]
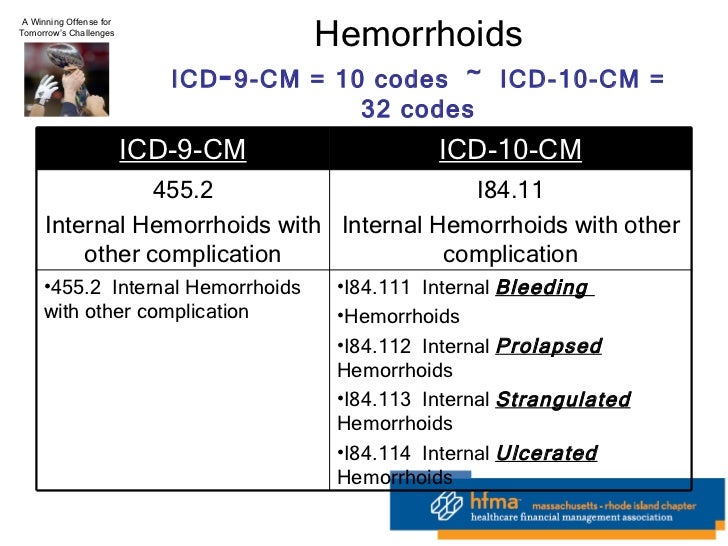 HFMA 1-21-11 On 5010 And ICD-10 | icd 10 suture removal
HFMA 1-21-11 On 5010 And ICD-10 | icd 10 suture removal[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="400"]
[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="960"]
[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="1030"]
[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="638"]
 ICD-10 Delay | icd 10 suture removal
ICD-10 Delay | icd 10 suture removal[/caption]
[caption id="" align="aligncenter" width="960"]
[/caption]