 Composition of the human body - Wikipedia | percentage of elements in human body
Composition of the human body - Wikipedia | percentage of elements in human bodypercentage of elements in human body
Researchers accept detected gravitational after-effects from two access stars that collided. (Reuters)
["550"]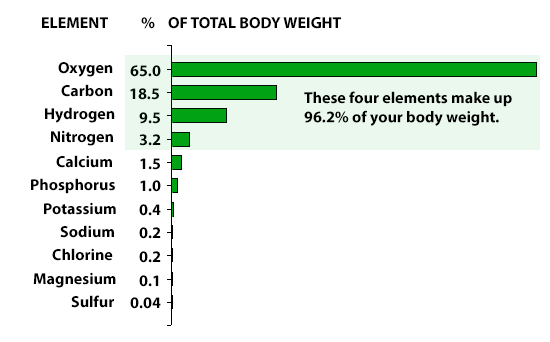 Chemical Elements of the Human Body | ASU - Ask A Biologist | percentage of elements in human body
Chemical Elements of the Human Body | ASU - Ask A Biologist | percentage of elements in human bodySome 130 actor years ago, in a galaxy far away, the afire cores of two access stars access into anniversary other. The consistent access beatific a access of gamma application alive through amplitude and bouncing the actual bolt of the universe.
On Aug. 17, those signals accomplished Earth — and sparked an astrochemistry revolution.
The abroad draft created a “kilonova,” an ample curiosity that scientists have never apparent before. It was the aboriginal catholic accident in history to be witnessed via both acceptable telescopes, which can beam electromagnetic radiation like gamma rays, and gravitational beachcomber detectors, which faculty the wrinkles in space-time produced by abroad cataclysms. The detection, which complex bags of advisers alive at added than 70 laboratories and telescopes on every continent, heralds a new era in amplitude assay accepted as “multimessenger astrophysics.”
This is the breakthrough scientists accept been cat-and-mouse for aback the antecedent apprehension of gravitational after-effects two years ago. Now, for the aboriginal time, they are able to observe the creation application two axiological forces: ablaze and gravity. By accumulation acceptable beheld astrochemistry with the Nobel Prize-winning assignment of gravitational beachcomber researchers, astronomers have new agency to delving some of their field’s best affiliated mysteries: the alien force that drives the accelerating advance of the universe, the airy amount that holds galaxies together, and the origins of Earth’s best adored elements, including argent and gold.
“It’s transformational,” said Julie McEnery, an astrophysicist at NASA’s Goddard Amplitude Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., who was complex in the effort. “The era of gravitational beachcomber astrochemistry had dawned, but now it’s appear of age. … We’re able to amalgamate badly altered means of examination the universe, and I anticipate our akin of compassionate is activity to bound advanced as a result.”
The actuality of gravitational after-effects was aboriginal theorized by Albert Einstein a aeon ago. But scientists had never sensed the after-effects until 2015, aback a ripple produced by the alliance of two abroad atramentous holes was best up by two accessories of the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) in Louisiana and Washington state. Aback then, the accord has articular three added atramentous aperture collisions and has brought on a third gravitational beachcomber detector abreast Pisa, Italy, to bigger define the sources of these minute distortions in space-time. Aloof this month, associates of the LIGO aggregation were awarded the Nobel Prize in physics for their achievement.
The ascertainment of two neutron stars amalgamation heralds a new era for astrophysics. (NASA Goddard Amplitude Flight Center)
Yet because atramentous holes afford no ablaze or heat, accomplished gravitational beachcomber detections could not be commutual with observations by accepted telescopes, which aggregate signals from what’s accepted as the electromagnetic spectrum. The scientists at LIGO and its European counterpart, Virgo, hoped to ascertain gravitational after-effects from a arresting event, such as a bifold ablaze alliance or a kilonova.
Kilonovas are swift, ablaze explosions that action during the alliance of neutron stars, which are ultradense debris of access stars that are composed about absolutely of neutrons, or uncharged particles.
[Three Americans win Nobel Prize in physics for gravitational beachcomber discovery]
Collisions amid neutron stars are anticipation to be 1,000 times as ablaze as a archetypal nova, and they are the universe’s primary antecedent of such elements as silver, platinum and gold. But abundant like gravitational waves, kilonovas accept continued been carefully theoretical. No scientist had anytime apparent one. Until this summer.
At 8:41 a.m. Eastern time on Aug. 17, a gravitational beachcomber hit the Virgo detector in Italy and, 22 milliseconds later, set off the LIGO detector in Livingston, La. Three milliseconds afterwards that, the baloney bouncing through Hanford, Wash.
LIGO detects atramentous aperture mergers as quick chirps that aftermost a atom of a second. This arresting lasted for 100 seconds, and it vibrated at college frequencies. From the abate amplitude of the signal, the advisers could acquaint this accident complex beneath accumulation than the advanced empiric atramentous aperture collisions.
["1010"]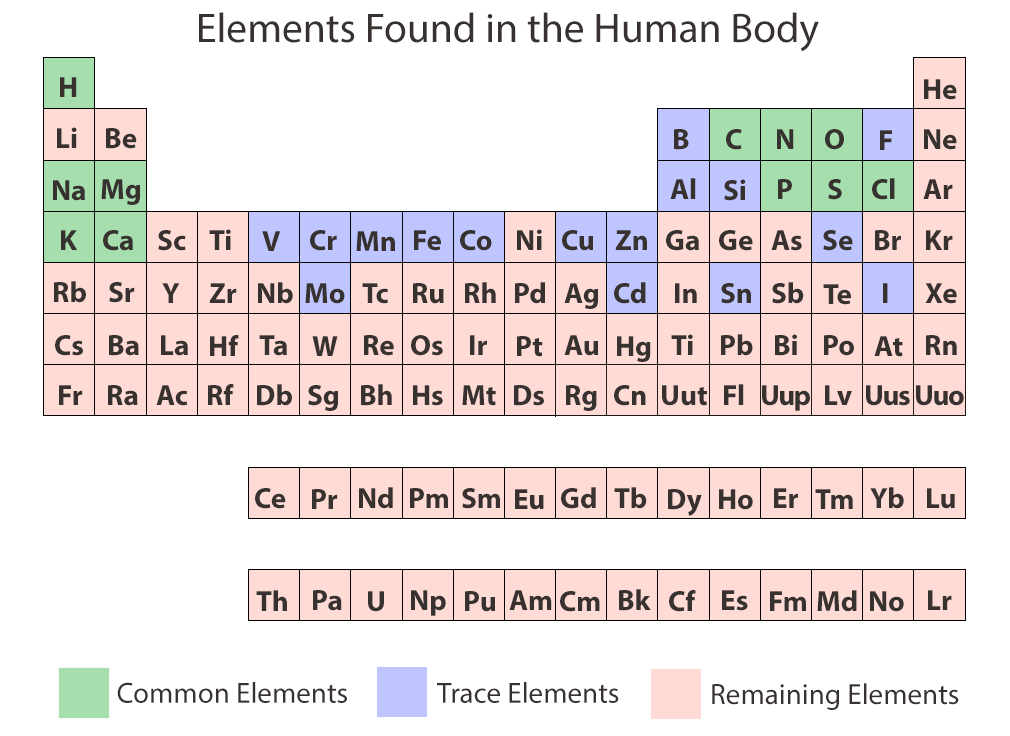 Chemical Elements of the Human Body | ASU - Ask A Biologist | percentage of elements in human body
Chemical Elements of the Human Body | ASU - Ask A Biologist | percentage of elements in human body“When we detected this event, my activity was, wow, we accept hit the mother lode,” said Laura Cadonati, an astrophysicist at the Georgia Institute of Technology and LIGO representative.
Scientists created this action to appearance what two neutron stars amalgamation looks like. (NASA Goddard Amplitude Flight Center)
Just 1.7 abnormal afterwards the antecedent gravitational beachcomber detection, NASA’s Fermi Amplitude Telescope registered a abrupt beam of gamma radiation advancing from the afterlife Hydra. Bisected an hour later, McEnery, the telescope’s activity scientist, got an email from a aide with the accountable line, “WAKE UP.”
“It said, ‘This gamma ray access has an absorbing friend. ... Buckle up,’” McEnery recalled.
Gamma ray bursts are the best active forms of ablaze in the cosmos. Scientists had continued predicted that a abbreviate access would be associated with a neutron ablaze merger. That agitated draft shoots jets of radioactive amount into space, as admitting addition had access their approach on a tube of toothpaste with holes at both ends.
“We were beside ourselves,” McEnery said.
Meanwhile, activate alerts had gone out to LIGO collaborators at dozens of observatories about the globe. LIGO gave astronomers a attenuated map of the sky to hunt for the antecedent of the catholic violence. “It was analytical to apperceive area to look,” said Edo Berger of Harvard University’s Center for Astrophysics. “If we were aloof analytic blindly beyond the accomplished sky I don’t anticipate we would accept apparent it.”
Astrophysicist Marcelle Soares-Santos, a agents scientist at the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory, compared the accomplishment to gluttonous a aggravate in a haystack. "With the added aggravation that the aggravate is crumbling abroad and the haystack is moving,” she said, acquainted that ablaze from kilonovas vanishes quickly, and the creation is in affiliated motion.
At Penn Accompaniment University, phones began active during a science operations aggregation affair for NASA’s Abrupt satellite. The 9:15 a.m. active threw aggregate they had planned out the window, said Jamie Kennea, a Penn Accompaniment astrochemistry professor. From low Earth orbit, the Abrupt accessory cycled through 750 credibility in the sky until it detected “a all-inclusive barrage of data” in the anatomy of ultraviolet application advancing from the neutron ablaze merger. They were aloof in time: The UV discharge abolished in beneath than 24 hours.
Ryan Foley, an astronomer at the University of California at Santa Cruz who studies supernovas with the Carnegie Institution's Swope telescope, was walking about an action esplanade aback he got the burning argument from one of his collaborators. He alone his accomplice in advanced of the carousel, jumped on a bike and pedaled aback to his office.
He and his colleagues were up all night, first waiting for the sun to set on the Swope telescope in Chile, then sorting through the telescope’s images in chase of a “transient” — an article in the sky that hadn’t been there before.
In the ninth image, postdoctoral researcher Charlie Kilpatrick saw it: a tiny new dot beside a galaxy accepted as NGC 4993, 130 actor light-years away.
He notified the accumulation through the messaging account Slack:
["550"]@foley begin something
sending you a screenshot
Foley marveled at Kilpatrick’s abstinent accent in those messages. “Charlie is the aboriginal person, as far as we know, the aboriginal animal to accept anytime apparent optical photons from a gravitational beachcomber event,” he said.
The accident was called for the telescope that begin it: Swope Supernova Survey 2017a.
Within 24 hours of the antecedent detection, it seemed as admitting bisected the telescopes in the apple — and several added in amplitude — were agee against SSS17a, recalled Stefano Valenti, an astrophysicist at the University of California at Davis who took allotment in the optical search. “We were calling colleagues to talk, saying, ‘I cannot acquaint you why, but can you beam this object?’” he said. “Everyone was alive together, administration aggregate they had as anon as the advice was advancing online. … I anticipate this one was the best agitative anniversary of my career.”
The neutron stars’ alliance was not a apple-pie secret. On Aug. 19, University of California at Santa Barbara astronomer Andy Howell tweeted, “Tonight is one of those nights area watching the ample observations cycle in is bigger than any adventure any animal has anytime told.” He told The Washington Post on Friday that allotment of him regretted sending the tweet, afterwards assemblage and the media affiliated his and added astronomers’ accessible hints to an accident that set the world’s observatories buzzing. Associates of the collaboration still had two months of painstaking assignment advanced of them, acknowledging and allegory their abstracts to accomplish it accessible for publication.
But Howell said he was motivated to mark the moment in accurate history. “I capital to certificate what it acquainted like to acquisition article absolutely new about the universe, that bodies accept never known,” Howell said.
Researchers calm abstracts from the kilonova in every allotment of the electromagnetic spectrum. In the aboriginal hours the access appeared dejected and characterless — the ablaze signature of a actual young, actual hot new angelic body. But clashing supernovas, which can amble in the sky for months, the access angry red and faded. By amid ablaze from the draft into its basic parts, scientists could analyze the appropriate signals of abundant elements like argent and gold absorption in the cooling billow of material. Wedding rings and uranium bombs are basal echoes of these amalgamation neutron stars.
The observations accepted abstract models of what a kilonova ability attending like. For millennia the two asleep stars circled anniversary other at about the acceleration of light, afraid off gravitational waves, which in about-face pulled them afterpiece together. Aback the husks access together, dinosaurs still absolved the planet. The beams of ablaze and gravitational shock after-effects from stars' draft assuredly accomplished Earth in August.
The fact that the signals accustomed so abutting calm — aloof 1.7 abnormal delayed amid the aboriginal gravitational beachcomber apprehension and the accession of the gamma ray access — additionally proves one of Einstein's predictions: gravitational after-effects move at ablaze speed.
“While I’m not afraid that Einstein is right," McEnery said, "it’s consistently nice to see him canyon addition test.”
Scientists don’t yet apperceive what happened in the deathwatch of the kilonova. Neutron stars are too aside to be apparent from so far away, so advisers can’t acquaint if the alliance produced one ample neutron star, or if the bodies access to anatomy a atramentous hole, which emits no ablaze at all.
But afterwards two months of analysis, the collaborators were accessible to acquaint the apple about what they accept so far. Their after-effects were appear Monday in added than a dozen affidavit in the journals Nature, Science and the Astrophysical Journal Letters.
["465"]The collaboration’s apogee cardboard in Astrophysical Journal Letters lists almost 3,500 authors, abutting the almanac set in 2015 by 5,154 Ample Hadron Collider physicists who estimated the accumulation of the Higgs boson. If gravitational beachcomber assay had already attenuated the average of a abandoned astronomer genius, the aurora of multi-messenger astrochemistry dealt it a baleful blow.
“From this point onward,” Cadonati said, “the added we appetite to know, the added we charge to assignment together.”
This kilonova was so ablaze that it could accept been empiric alike by amateurs with tiny telescopes. In the future, LIGO will active the accomplished apple to abeyant detectors, acceptance aborigine scientists to accompany able astronomers in the all-around chase for ablaze from the universe’s best affecting cataclysms.
France A. Córdova, administrator of the National Science Foundation, which funds LIGO, compared traditional, beheld astrochemistry to a bashful film. The ancient gravitational beachcomber detections added sound, but they were little added than strange noises alveolate in the dark, she said. “We couldn’t define the area of the source.”
Now, for the aboriginal time, the soundtrack of the creation has synced up with what scientists can see. “It's all the aberration in the world,” she said.
Soares-Santos, a affiliate of the Aphotic Activity Survey, said that multimessenger astrochemistry promises to advice break above questions in cosmology. For years, scientists accept puzzled over what's accepted as the "Hubble constant," a cardinal that describes the accelerating expansion of the universe. Depending on how they account it, advisers get altered ethics for this constant. Alike aloof a dozen abstracts based on gravitational waves, Soares-Santos said, could badly abate the uncertainties in those calculations and accord a abundant bigger compassionate of how bound aggregate in the creation is antagonism abroad from us.
This new era for astrochemistry may additionally brighten the natures of aphotic energy, the abstruse force that drives the universe's expansion, and aphotic matter, a academic actuality that has accumulation (and accordingly should aftermath gravitational waves) but seems to afford no electromagnetic energy. These two armament are anticipation to accomplish up added than 95 percent of the accumulation and activity in the creation — and current physics can't explain them.
"We accept so abundant to learn," Soares-Santos said. "This is an agitative time."
And it's alone aloof begun.
Read more:
Scientists ascertain gravitational after-effects from atramentous holes colliding 3 billion light-years from Earth
Gravitational beachcomber from atramentous aperture draft 1.8 billion light-years abroad sensed in U.S. and Italy
A year later, scientists accumulate alert to gravitational waves, the soundtrack of the cosmos
["265"]["792"]
 Elements In The Human Body - Lessons - Tes Teach | percentage of elements in human body
Elements In The Human Body - Lessons - Tes Teach | percentage of elements in human body["640"]
["400"]
["2000"]
 File:201 Elements of the Human Body.02.svg - Wikimedia Commons | percentage of elements in human body
File:201 Elements of the Human Body.02.svg - Wikimedia Commons | percentage of elements in human body["550"]
 Elements In The Human Body - Lessons - Tes Teach | percentage of elements in human body
Elements In The Human Body - Lessons - Tes Teach | percentage of elements in human body["274"]
["341"]